
Environment and Geology Beautiful Weathering structure on the rocks around Ranchi city, India.
Last updated 22 Mar 2021 Share : Weathering is the breakdown of rocks in situ. There are three types of weathering; physical, chemical and biological. The rate that weathering occurs at will depend on the rock type, the climate and the relief. Physical weathering Physical weathering is also known as mechanical weathering.

Groningen RKCBlauwe haai [39+] Weathering Definition Geography Gcse
The complete loss of particular atoms or compounds from the weathered surface. (2). The addition of specific atoms or compounds to the weathered surface. (3). A breakdown of one mass into two or more masses, with no chemical change in the mineral or rock. The residue of weathering consists of chemically altered and unaltered materials.

Biological Weathering Definition, Process, Types & Examples
There are three types of weathering: mechanical, biological, and chemical. Mechanical weathering is caused by wind, sand, rain, freezing, thawing, and other natural forces that can physically alter rock. Biological weathering is caused by the actions of plants and animals as they grow, nest, and burrow. Chemical weathering occurs when rocks.
/examples-of-chemical-weathering-607608_FINAL-54f8c4d63ed94e0eab454dc5e96cabff.png)
4 Types and Examples of Chemical Weathering
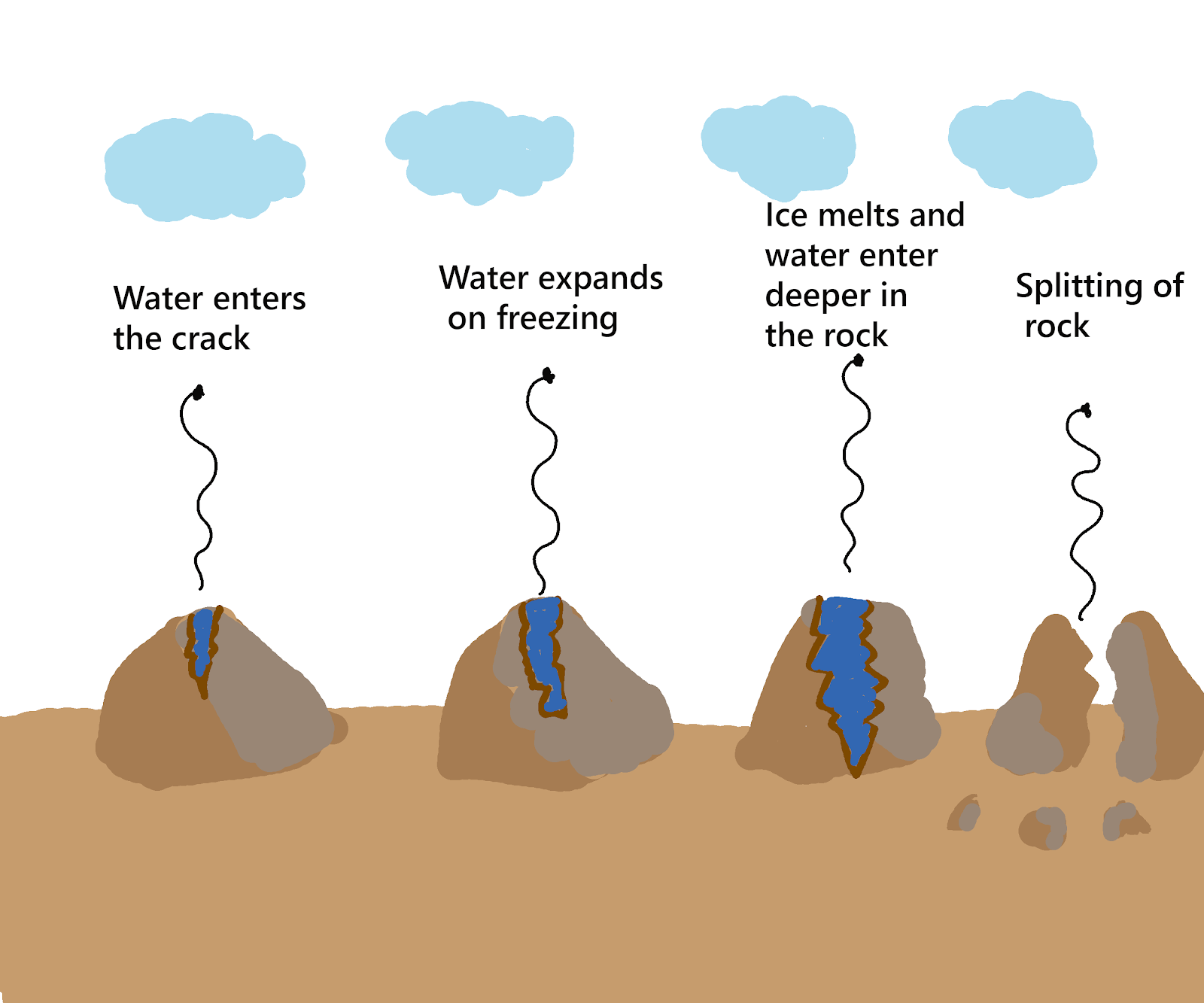
biological weathering root wedging animal burrowing. Frost Wedging A diagram displaying the steps of frost wedging One type of physical weathering is frost wedging. Frost wedging occurs when liquid water seeps into pores and small cracks in the earth and expands when it freezes. This causes the cracks to enlarge.

BIOLOGICAL WEATHERING & ITS TYPES YouTube
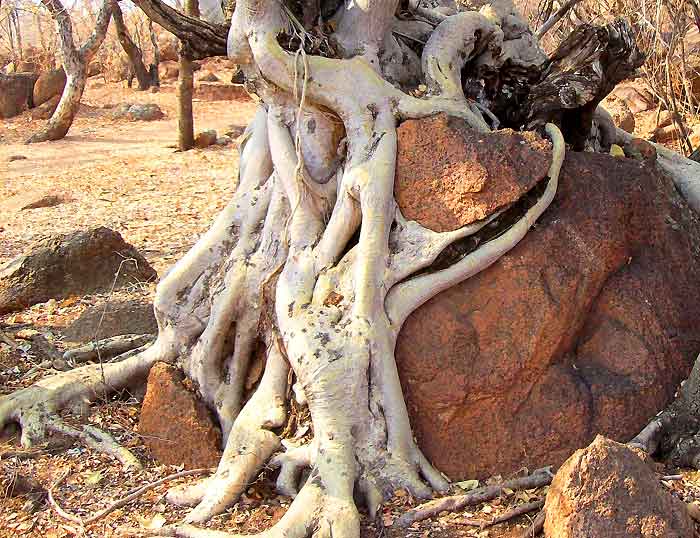
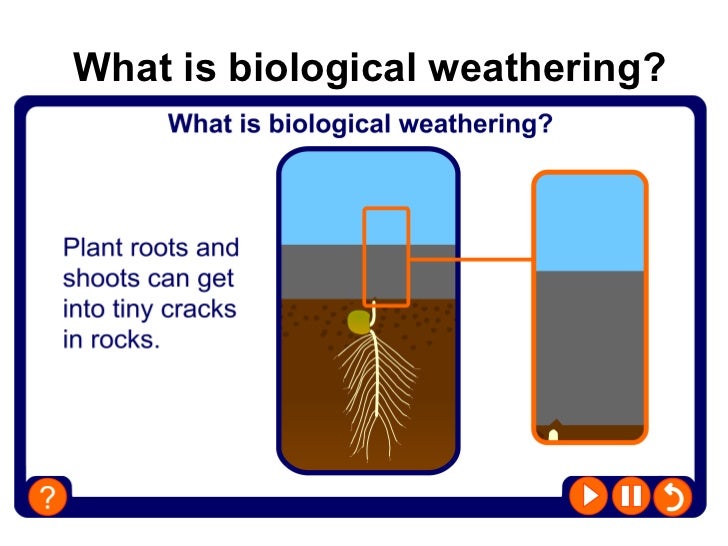
Biological Weathering. Living organisms contribute to the weathering process in many ways: Trees put down roots through joints or cracks in the rock in order to find moisture. As the tree grows, the roots gradually prize the rock apart. Many animals, such as these Piddock shells, bore into rocks for protection either by scraping away the grains.

Figure 1 from Biological weathering and its consequences at different spatial levels from
The carbon cycle is represented in the following diagram: To help us understand the carbon cycle, we can think of it as two interconnected subcycles: a biological carbon cycle and a geological carbon cycle. Biological carbon cycle

BG Reviews and syntheses Biological weathering and its consequences at different spatial
As its name suggests, biological weathering is a type of weathering brought about by various activities of living organisms.

Weathering
What are the biological processes of weathering? | American Geosciences Institute What are the biological processes of weathering? Living things also help form soil. Once rock is weathered into smaller particles, microorganisms and small plants begin to establish themselves there.

Freeze Thaw Weathering Geography Wiki Beyond Twinkl
Biological weathering only refers to weathering caused by organisms -- animals, plants, fungi and microorganisms such as bacteria. While certain forms of biological weathering, such as the breaking of rock by tree roots, are sometimes categorized as either physical or chemical, biological weathering can be either physical or chemical.

Biological weathering Biological weathering, Plant roots, Animal action
Weathering involves physical and chemical processes that are modified by biological activity of plants, microorganisms and animals. This article reviews recent progress made in understanding biological processes contributing to weathering.
02 types of weathering
Humans Biological Weathering Causes 1. Roots Of Plants Some trees grow inside of rocks, which aids in biological weathering. Roots of plants and trees delve into the soil in quest of moisture and nutrients. The joints or cracks in the rocks are traversed by the roots as they move through the soil, gradually rupturing the rock.
Coastal Transportation and Deposition GCSE Geography Revision Notes
Biological weathering. Plants and animals can also have an effect on rocks. Roots burrow down, weakening the structure of the rock until it breaks away.

Geology Chemical weathering, 6th grade science, Earth science
(1) Physical weathering, (2) Chemical weathering, and (3) Biological weathering or biogeochemical weathering. 1. Physical Weathering: Physical weathering of rocks is a mechanical process which is brought about by a number of factors, such as: ADVERTISEMENTS: (A) Temperature, (B) Water, (C) Wind. (A) Temperature:

PPT Coastal erosion processes PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2049508
Biological weathering occurs when plants break up rocks with roots or root exudates. The process is slow, but may strongly influence landscape formation. Biological weathering increases with soil thickness until optima for biotic activity are reached, but decreases when soils get thicker and biotic activity has less influence on weathering.

Weathering 8 8 0 Weathering Learning Intentions You
Weathering is the process of disintegration of rock from physical, chemical, and biological stresses. Weathering is influenced by temperature and moisture (climate).. A conceptual diagram showing how weathering breaks down rocks and minerals; eventually, soil formation begins in place.

Weathering and river discharge surprisingly constant during Ice Age cycles
Biological weathering occurs via the development of biofilm on biochar's surface,80 which can alter the performance of biochar in removing contaminants. 39 Biofilm is defined as a broad community of microorganisms-single or multiple species of gram-positive and/or gram-negative bacteria-that grows irreversibly attached to a surface depending on.